There are many different types of gears in the industry. In this post, we will discuss the 5 most important types of gears (in no particular order) and where they are used.
5 Common Types of Gears
Spur Gear
Spur gears are easy to visualise as they have straight teeth and are mounted on parallel shafts. As a result of being mounted on parallel shafts along with a straight edge of the teeth, no axial thrust force is generated, as seen with some other gears. Spurs gears are easy to produce, which allows a higher precision manufacturing process. When spur gears mesh with each other, they tend to generate an impact noise as the meshing teeth collide. The stress on the gear teeth is impacted negatively by this.

Helical Gear
Helical gears are similar to spurs gears as they are both mounted on parallel shafts. However, the cut of the helical gear teeth is at an angle to the gear face, unlike spur gears. The angled gear teeth have a positive influence on tooth stress. It allows for a gradual engagement of meshing teeth, allowing for a better distribution of stresses, minimising stress concentrations. The gradual meshing of the teeth allows helical gears to produce a lot less noise than spur gears. Low noise levels and smoother engagement is the primary reason why helical gears are attractive for car transmissions. Unlike spur gears, helical gears produce and axial force when meshing due to the angled teeth. As a result, when helical gears are used, it is common to see bearings capable of supporting axial loads, e.g. angular contact bearings.
As time has developed, helical gears have been used more often making them one of the most important types of gears.
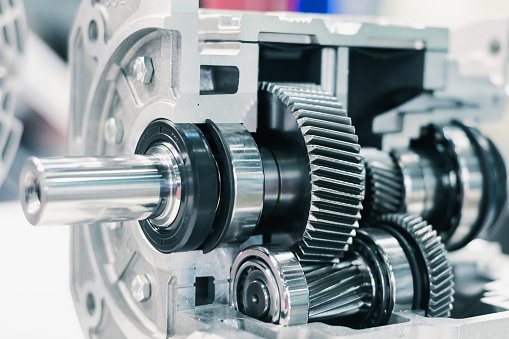
Bevel Gear
Bevel gears are required in scenarios where shafts are 90 degrees to each other. However, they can also operate at other angles. Bevel gears are of a conical shape and can have straight cut teeth, like spur gears, or angled cut teeth, like a helical gear. Bevel gears that have helical teeth (seen below) are used in car differentials. This type of gear is known as a spiral bevel gear.

Like spur gears and helical gears, depending on what type of teeth the bevel hear has will determine the noise of engagement and thrust forces generated.
Worm gear
Worm gears are mated with a screw shape cut on a shaft, known as the worm. Worm gears allow for a large gear reduction which makes it an attractive proposition for uses in conveyors. It is not unusual for worm gears to provide gear reductions of 20:1 up to 300:1. Changing the ratio requires the circumference of the gear to be increased or decreased.
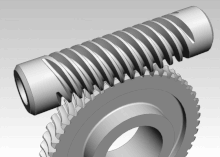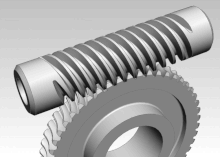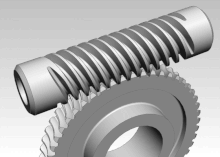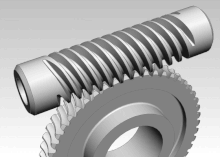
The gear is driven by the worm, but the gear cannot drive the worm. This is because the angle on the worm is shallow, which results in the gear not being able to overcome the friction, creating a self-locking feature.
Rack and pinion
Imagine a gear unravelled and laid in a straight line. A rack looks just like this (as seen in both images below). The use of a rack and pinion allows the conversion of rotational motion to linear motion.


A great visualisation, and realistic example, is in a car. When you are turning the wheel, you are turning the pinion. The rotating pinion moves the rack in a linear motion resulting in a force being exerted on the wheel assembly, turning the wheel. The force exerted on the rack is determined by the size of the pinion and its tooth pitch.
Which Is The Most Important Type of Gear?
All of the gears discussed here have an extremely important use within their system. To determine which type of gear is the most important, it depends on what is classified as important? How frequent it is used? How important the system is? The answer to this question is difficult and is down to how the person answering interprets important.
I hope you have enjoyed this post and learned 5 important types of gears. Please leave feedback and questions in the comments below.
Related Posts: Damage to Gears: The Different Types of Gear Wear
